Explain Why There Are Different Numbers of Atp Produced
This is one of the main purposes of glycolysis - to make electron carriers for the final stage. And movement of flagella.

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation
Although a few of the ATP utilized by cells is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation the majority is produced by oxidative phosphorylation which requires the.

. ATP Adenosine Triphosphate is the general currency of energy in cells it is what living cells utilize for activities requiring energy like muscle contraction. ATP is produced through several different methods. The NADs becomes NADH.
Here is how this 2 ATP gets produced. If however the malate-aspartate shuttle is used a total of 5 ATP is produced. 2 NAD electron carrierss enter and take 2 H one from each half.
It is the creation of ATP from ADP using energy from sunlight and occurs during photosynthesis. So the final stoichiometry is 1 NADHH. 25 ATP 1 FADH2.
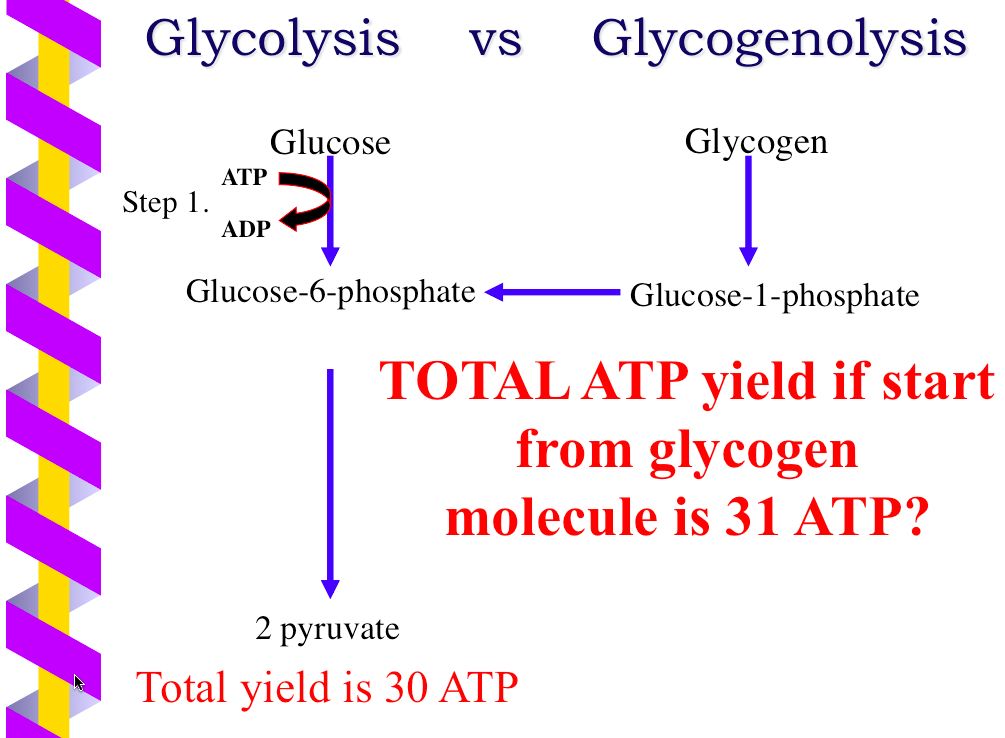
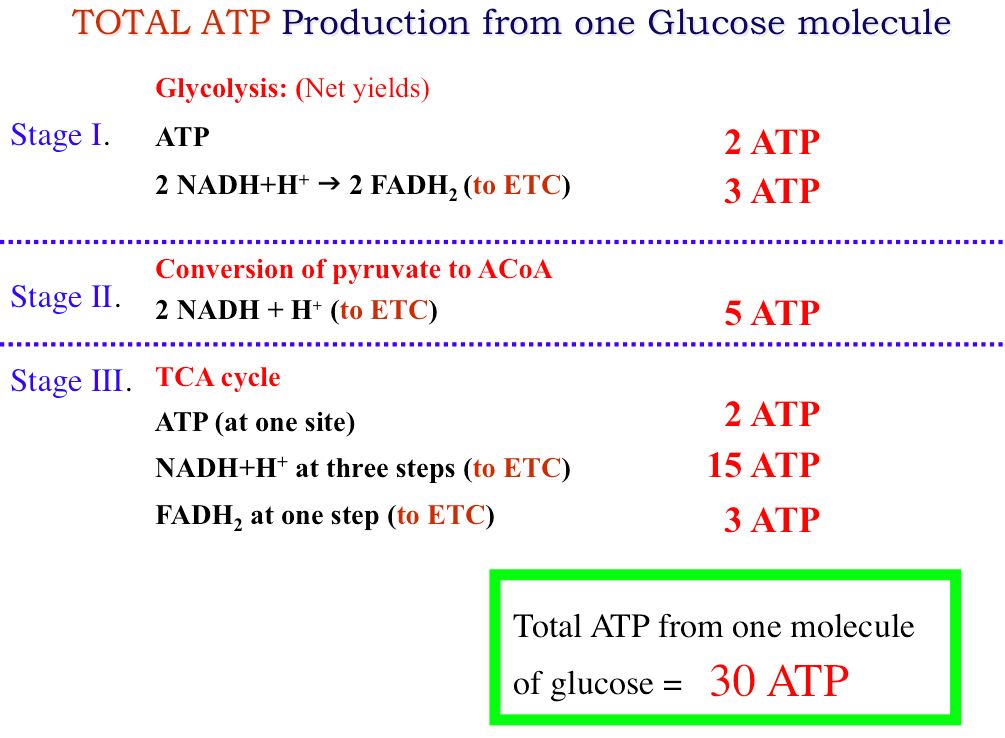
When each FADH 2 gives up electrons and hydrogen ions there is enough of a potential energy change to make two ATP molecules. Fill in the chart below to calculate the total amount of ATP produced from the breakdown of each glucose molecule during the three steps of cellular respiration. But when yeast metabolize glucose anaerobically only 2 molecules ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose.
Each stage of respiration contributes to the production of ATP. 2 ATP molecules each donate a phosphate group to each side of the glucose molecule. 2 FADH2 Mitochondria 15 3 ATP Total.
If the electrons from NADH are transferred to the Q-pool via the glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle only 3 ATP are produced. Because in aerobic respiratio View the full answer. The electrons carried through the NADH produced by the glycolysis and citric acid cycle and the FADH2 produced by citric acid cycle are taken for electron transport phosphorylation.
This completely oxidizes all carbons of glucose into CO2 and produces the maximum energy poss. 64 ATP 1 FADH2. Although the theoretical yield can be up to 38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose this yield is very rarely achieved.
When yeast metabolize glucose aerobically 32 molecules of ATPs are produced from one molecule of glucose. An enzyme cuts the sugar in half. So the correct answer is Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when FADH2 is the electron donor than when NADH is the.
The movement of H into the matrix is down the concentration gradient and so give the ATP synthase energy to form 26 - 28 ATP. In the mitochondria the metabolism of sugars is completed and the energy released is harnessed so efficiently that about 30 molecules of ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose oxidized. View the full answer.
Explain why are there different numbers of ATP produced when yeast metabolize. The H ions return to the matrix through transport proteins called ATP synthase. When metabolism of glucose is aerobic the end product of glycolysis pyruvate enters into the oxidative phosphorylation occurs in mitochondria.
By contrast only 2 molecules of ATP are produced per glucose molecule by glycolysis alone. Mitochondria can use both pyruvate and fatty acids as fuel. Two ATP molecules are used at the start of glycolysis to.
15 ATP ATP. In the process the 6 carbon atoms in the glucose molecules are split in half and three go in each pyruvate. There are 2 NADH produced in the second phase of the glycolysis.
This whole stage is called oxidative phosphorylation. Potential energy change to make three ATP molecules. And 4 protons needed by ATP synthase to make one ATP molecule.
Photophosphorylation is a method specific to plants and cyanobacteria. Scientists dont yet know exactly how many protons are pumped in the respiratory chain but the current estimates are. In addition 2 NAD are reduced to 2 NADH and a net gain of 2 ATP is produced.
Hence the total ATPs produced in an aerobic respiration is 2 2 32 36. In this process 32 ATP molecules are produced. 104 ATP 1 NADHH.
Up to 256 cash back 3Explain why fermentation is necessary in cells that do not have access to oxygen â talk about the role of NADH. 6Products of photosynthesis are. Interestingly overexpression of wild-type AGCs but not mutants lacking the Ca 2-binding sites enhanced the upregulation of ATP production upon cell stimulation confirming that different Ca 2-effectors enzymes carriers located in different mitochondrial fractions matrix intermembrane space may cooperate in ATP-producing capacity.
Finally oxygen molecules O 2 accept the e and H and form water molecules. Describe the production of ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation in different stages of respiration with reference to the number of ATP molecules produced. NADHH coming from glycolysis ratio during the.
ATP can be produced in various ways. ATP is formed through substrate-level phosphorylation which is when an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP which forms ATP. 10 protons pumped by NADH.
ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. 4For what is the NADH and FADH2 produced during the Krebs cycle used. The 2 NADH they produce enters the same step of the ETC as the other NADH meaning they get 25 ATPall NADH so add an extra 2 to the glycolysis NADH for a total of 32 ATP.
It is important to consider at which stages the losses of ATP occur and whyOnce 2 net molecules of ATP are produced after glycolysis which occurs in the cytoplasm pyruvate must be transported into the mitochondrial matrix where the next stage will take. Coli is bacteria and bacteria use their plasma membranes to establish a proton gradient for the electron transport chain. What are the products of cellular respiration.
As NADH starts it with complex I it has more chance to pump proton across the gradients which increase the ATP synthase and hence produce more ATP than FADH which collects two protons by reducing its path to complex II. One factor underlying this variation is that the amount of H pumped into the inter-membrane space per unit of oxygen consumed by the ETC the H O ratio is substrate-specific. This means that each NADH can make 25 ATPs 104 and each FADH can make 15 ATPs 64.
Although ATP production depends on the rate of oxidation the number of ATP molecules produced for each oxygen atom consumed by the mitochondria termed the PO ratio can vary.

Cellular Respiration Takes In Food And Uses It To Create Atp A Chemical Which The Cell Uses For Energy
No comments for "Explain Why There Are Different Numbers of Atp Produced"
Post a Comment